Whether you have a few dozen certificates or a few thousand, you need to be able to manage them easily. We'll help you do this by showing you the certificates that are installed on the hosts in your environment using an easy to search inventory. Just go to VM/VMDR > Assets > Certificates.
Certificates stored in Vulnerability Management are intended to be an inventory of all certificates found from QID 86002 and can be manually removed from the inventory if no longer active or relevant. Through a vulnerability report, using QID 86002, you can get only those certificates that are currently detected. To get an active list of all certificates, just run a CertView scan. Please contact your Technical Account Manager if you do not see CertView module enabled.
|
Get Started |
|
Step 1: Run new vulnerability scansStep 1: Run new vulnerability scans You have to run new vulnerability scans on your hosts with the following criteria. - The scan must be run using version 7.12 or later. We added capabilities in version 7.12 to gather and store certificate information for your account, allowing you to search and review your certificates. (To see SSL grades, you must run scans using version 8.5 or later.) - The scan must include SSL certificate QIDs. These QIDs are included automatically if you run a complete vulnerability scan. Make sure to include them if you run a custom scan with only a select number of QIDs - just add a search list with the SSL certificate QIDs to your option profile. How do I find these QIDs? Just search the KnowledgeBase with these criteria: title "SSL Certificate" and category "General remote services". - (Optional) Enable the Additional Certificate Detection option in your option profile to find certificates in more locations on your hosts (not just ports). For example, find certificates in locations like Apache, Tomcat, Java KeyStore and Windows IIS. |
|
Step 2: Review your certificatesStep 2: Review your certificates Go to VM/VMDR > Assets > Certificates. Newly discovered certificates are added automatically to the inventory as new scan results become available in your account. Use the dashboard options at the top of the page to get a breakdown of your certificates - by expiration date, key size, certificate authority, and self-signed certificates. |
|
Good to Know |
|
Why don't I see the Certificates tab?Why don't I see the Certificates tab? The New Data Security Model must be enabled for the subscription in order for you to see certificates for your hosts. A Manager can enable the New Data Security Model by going to Users > Setup > Security. |
|
Why don't I see any certificates?Why don't I see any certificates? You may not see certificates for these reasons: 1) you haven't run any vulnerability scans using version 7.12 or later, 2) you did run scans but you did not include SSL certificate QIDs, 3) your scan results have not yet been processed, and 4) no certificates were found for your scanned hosts. |
|
Tell me about SSL gradesTell me about SSL grades (Available only when the SSL Labs Grade feature is enabled for your subscription.) SSL Labs has been integrated with Qualys VM to provide grades for your certificates. When enabled, you’ll see a letter grade (A+, A, A-, B, C, D, E, F, T, M, NA) for each certificate on your certificates list. This grade is intended to help you identify and prioritize certificates with SSL configuration issues. Learn more |
|
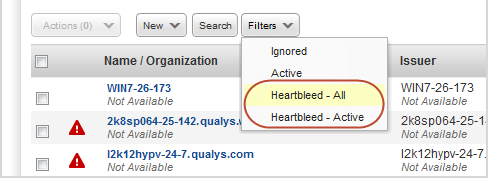
Heartbleed remediation reportingHeartbleed remediation reporting Use Heartbleed filters to find hosts affected by the Heartbleed bug. Select Heartbleed-All to see all affected hosts (active and fixed). Select Heartbleed-Active to see only hosts that are currently vulnerable. Learn more
|
|
Can I identify certificates by the fingerprint?Can I identify certificates by the fingerprint? Yes, you can add the certificate fingerprint to your certificates list. Click on the Tools menu (above the list on the right side), go to Columns and select Certificate Fingerprint. |